"Allulose Enhanced Intestinal Barrier Function and Tight Junction Regulation: Joint Research by Samyang Corporation and Chung-Ang University Published in International Scholarly Journal"
2023.08.28Samyang Corporation has announced that their research, in collaboration with Chung-Ang University Medical School, on the enhancement of intestinal barrier function and promotion of gut health by allulose, has been published in the internationally acclaimed Journal of Functional Foods.
On August 11th, a collaborative study conducted by Samyang and Chung-Ang University Medical School was published under the title "Allulose enhances epithelial barrier function by tight junction regulation via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB immune signaling pathway in an intestinal Caco-2 cell model."
The objective of this study by Samyang was to scientifically validate the positive impact of allulose on gut health. The study aimed to elucidate how allulose enhances the function of the intestinal epithelial barrier, with a specific focus on understanding the role of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB immune signaling pathway in this mechanism.
To evaluate the effects of allulose at different concentrations, the researchers utilized an intestinal Caco-2 cell model induced by LPS(Lipopolysaccharides, lipid oligosaccharides inducing barrier disruption and inflammation). The study findings revealed that allulose effectively reduced cellular toxicity caused by LPS and mitigated intracellular oxidative stress. Additionally, allulose treatment led to an increase in transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and a reduction in intestinal epithelial cell permeability. As a result, allulose facilitated the xssexpressi of junctional representative proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1, which are crucial for maintaining cell-cell connections in the intestinal epithelium. Furthermore, allulose demonstrated its potential to suppress inflammatory responses triggered by LPS by modulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB immune signaling pathway, thus contributing to improved gut health. (▲Fig 1)
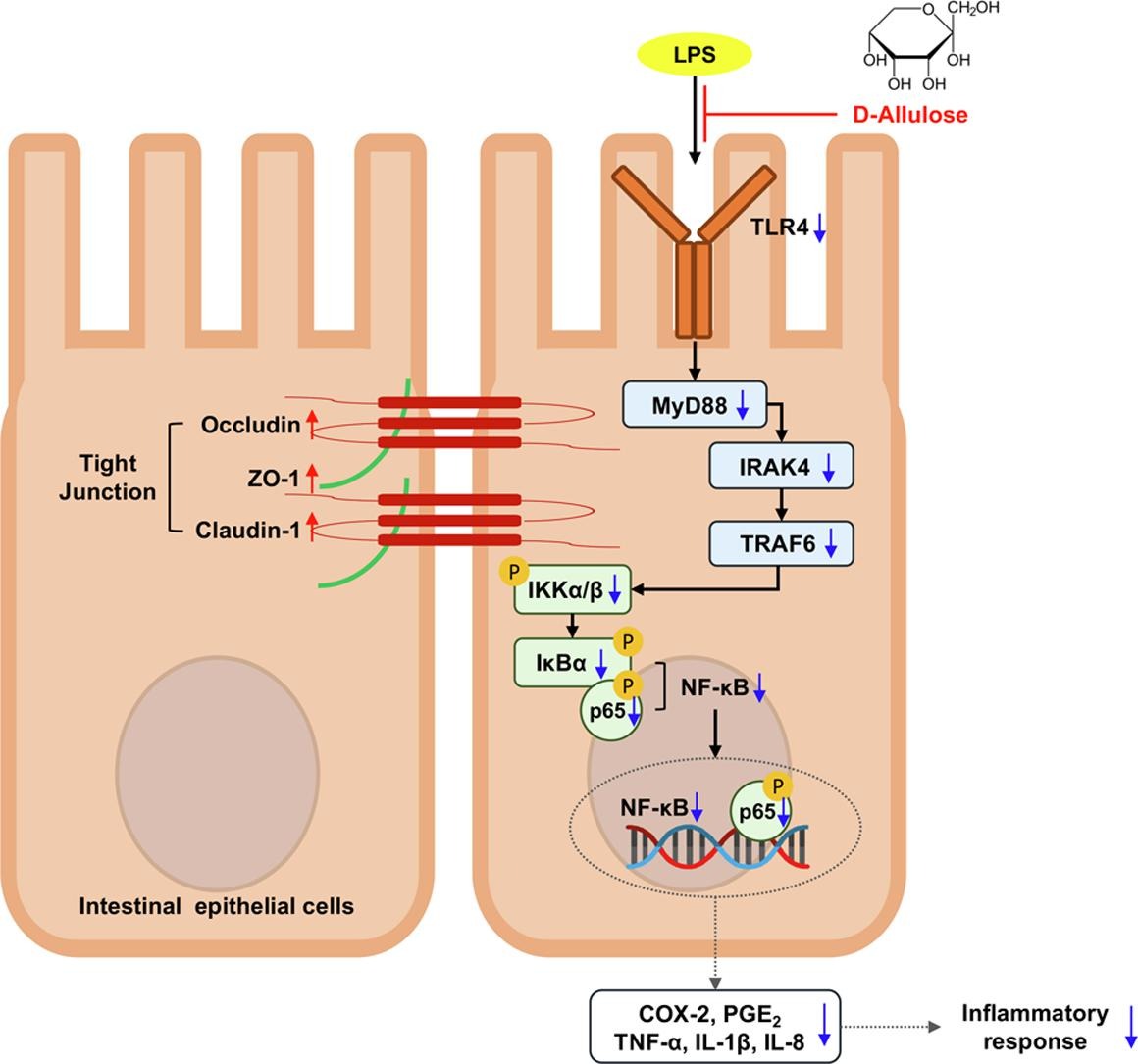
▲ Fig 1. A Mechanism of Allulose: Enhances intestinal Barrier Function and Tight Junction Regulation
A researcher from Samyang emphasized, "The outcomes of this study suggest that allulose may enhance gut health by improving intestinal epithelial cell functionality and suppressing inflammation through immune signaling pathways." They added, "Moving forward, Samyang intends to further validate the diverse functions of allulose through more in-depth preclinical and clinical trials."


